Switch#
The Switch node is used to route a workflow conditionally based on comparison operations. It is similar to the IF node, but supports up to four conditional routes.
Node Reference#
Mode: This dropdown is used to select whether the conditions will be defined as rules in the node, or as an expression, programmatically.
You can add comparison conditions using the Add Routing Rule dropdown. Conditions can be created based on the data type. The available comparison operations vary for each data type.
- Boolean
- Equal
- Not Equal
- Number
- Smaller
- Smaller Equal
- Equal
- Not Equal
- Larger
- Larger Equal
- String
- Contains
- Equal
- Not Contains
- Not Equal
- Regex
You can route a workflow when none of the specified conditions are met using Fallback Output dropdown list.
Example Usage#
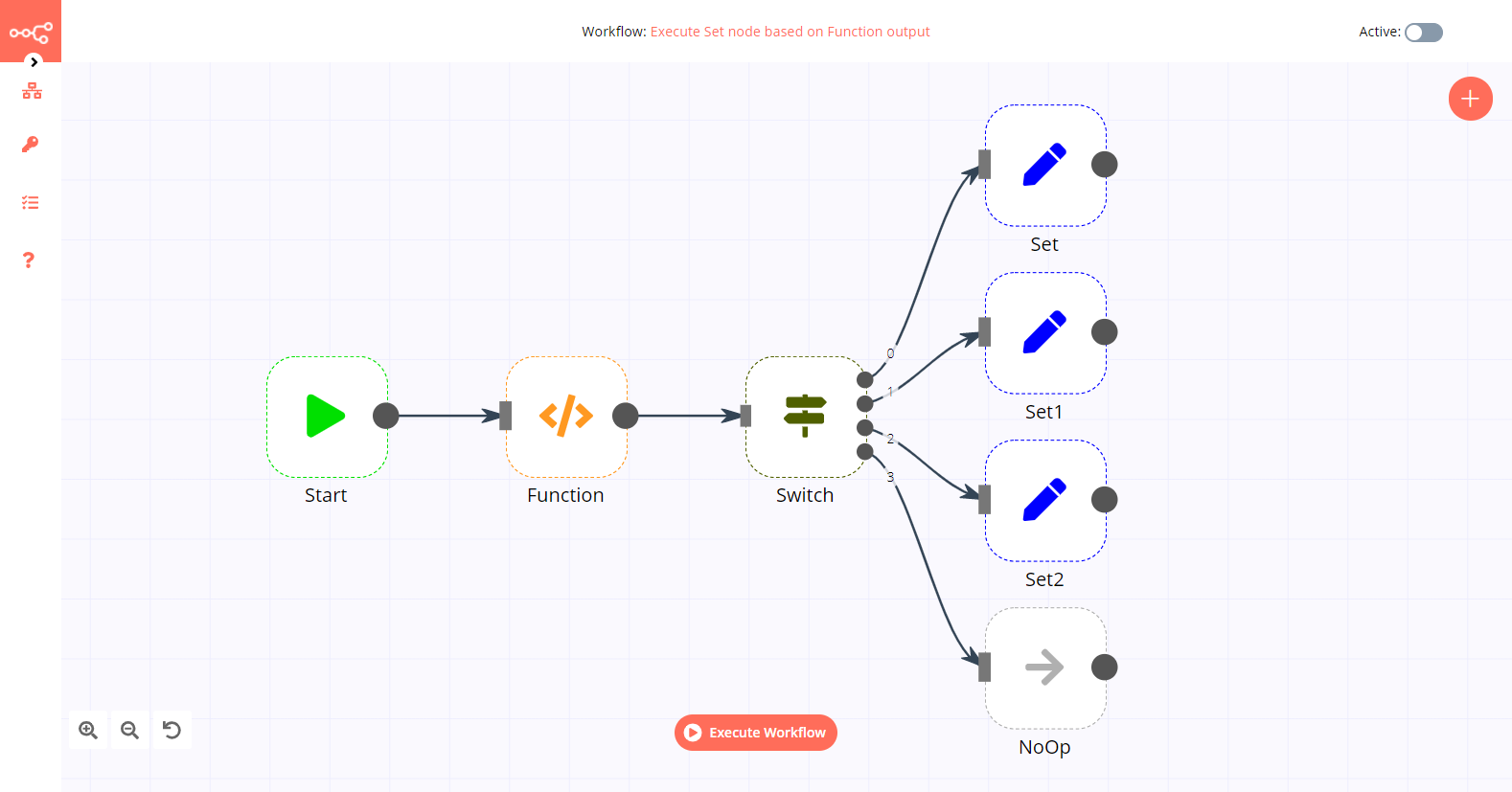
This workflow executes four different Set nodes based on the output given by a Switch node. You can also find the workflow on n8n.io. This example usage workflow would use the following nodes. - Start - Function - Switch - Set - NoOp
The final workflow should look like the following image.
1. Start node#
The start node exists by default when you create a new workflow.
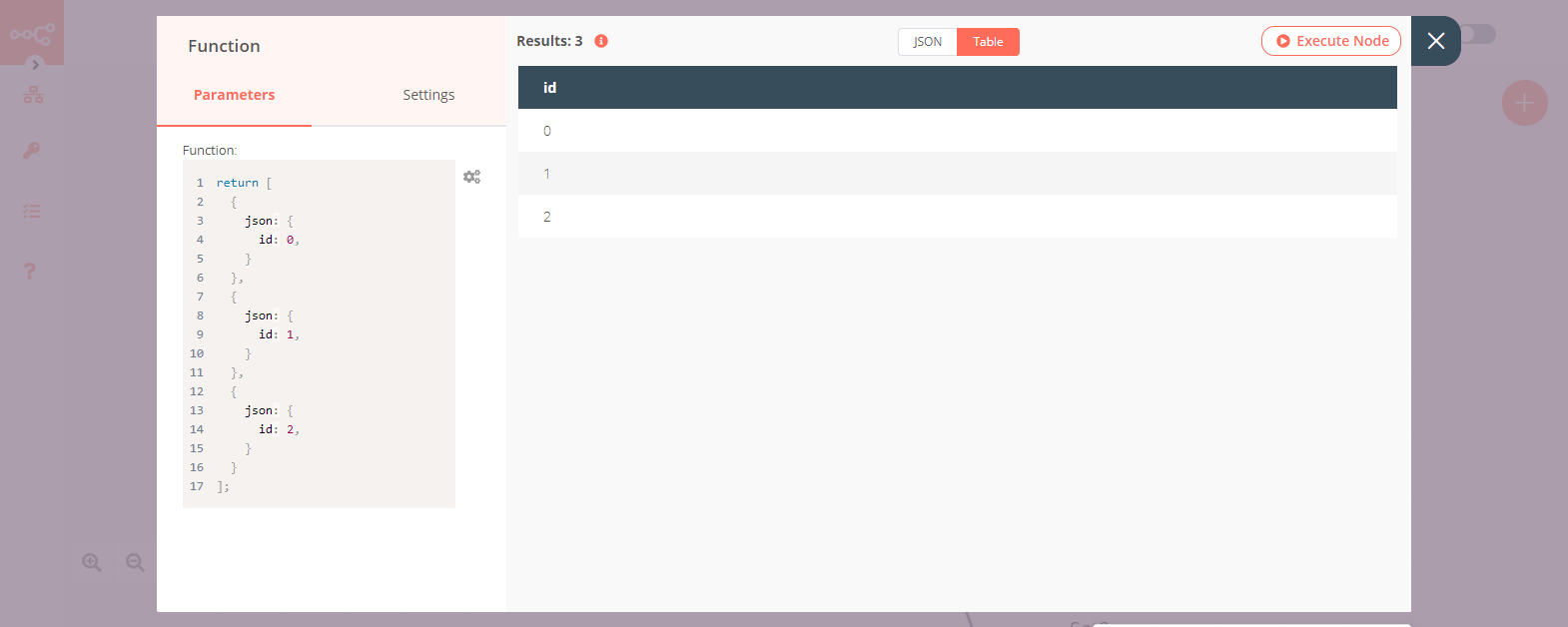
2. Function node#
- Enter the following code in the Function field.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
return [ { json: { id: 0, } }, { json: { id: 1, } }, { json: { id: 2, } } ]; - Click on Execute Node to run the workflow.
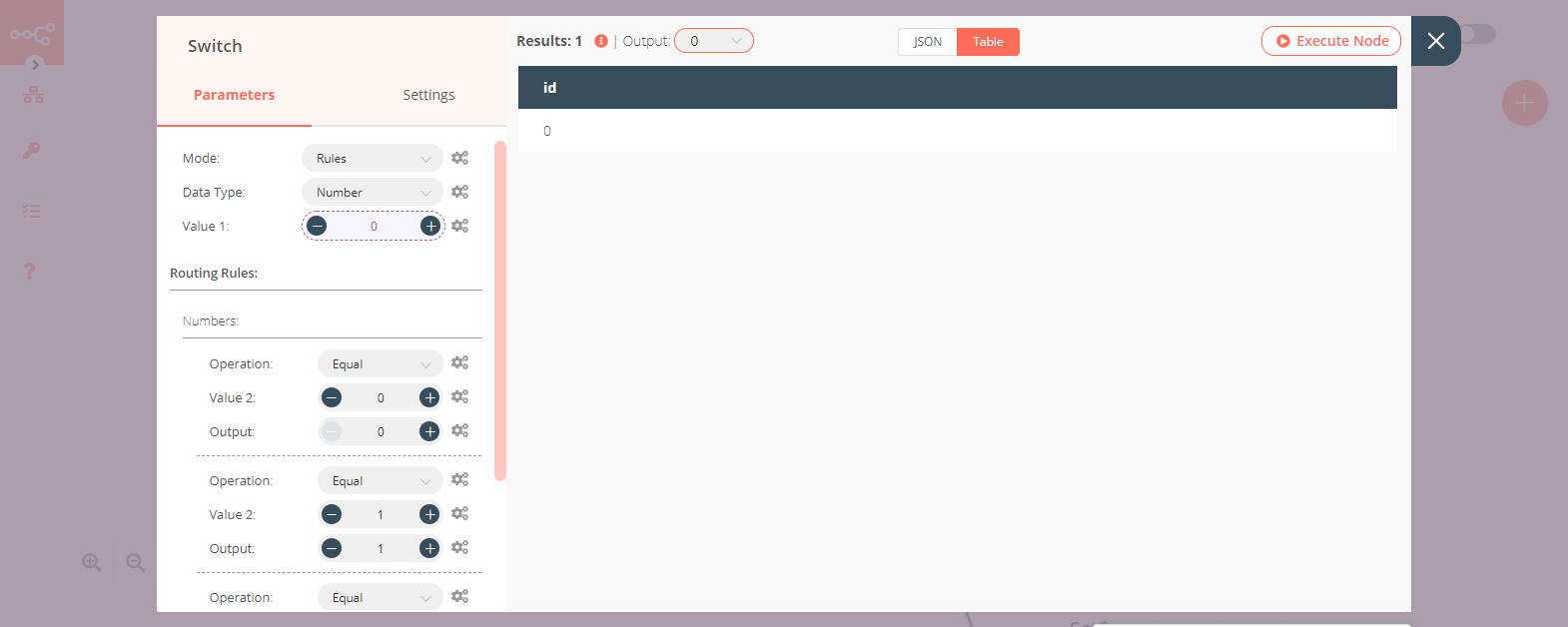
3. Switch node#
- Click on the gears icon next to the Value 1 field and click on Add Expression.
- Select the following in the Variable Selector section: Nodes > Function > Output Data > JSON > id. You can also add the following expression:
{{$node["Function"].json["id"]}}. - Click on the Add Routing Rule button.
- From the Operation dropdown list, select 'Equal'.
- Enter '0' in the Value 2 and the Output fields.
- Click on the Add Routing Rule button.
- From the Operation dropdown list, select 'Equal'.
- Enter '1' in the Value 2 and the Output fields.
- Click on the Add Routing Rule button.
- From the Operation dropdown list, select 'Equal'.
- Enter '2' in the Value 2 and the Output fields.
- Select '3' from the Fallback Output dropdown list.
- Click on Execute Node to run the node.
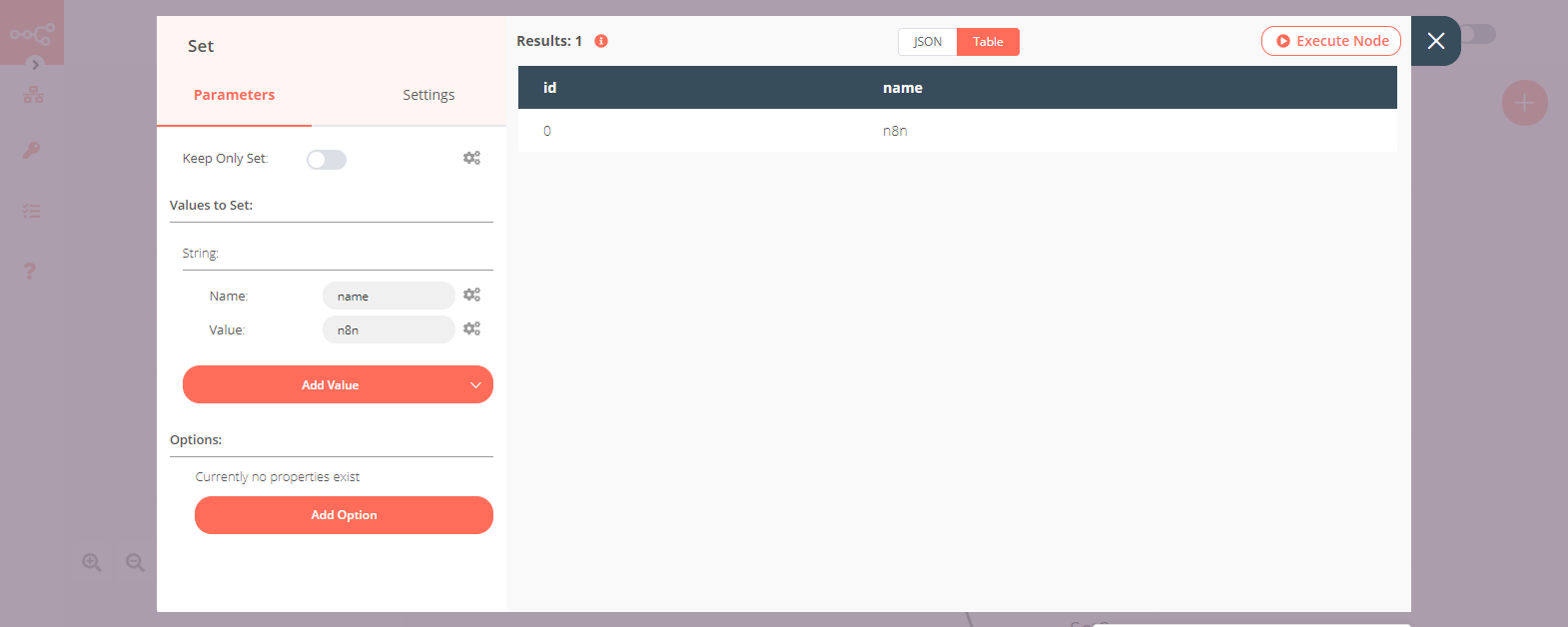
4. Set node (for '0' route)#
- Create a Set node connected to the '0' output of the Switch node.
- Click on the Add Value button and select 'String' from the dropdown list.
- Enter
namein the Name field. - Enter
n8nin the Value field. - Click on Execute Node to run the node.
Note: Notice that only the id with the value 0 made its way to this Set node.
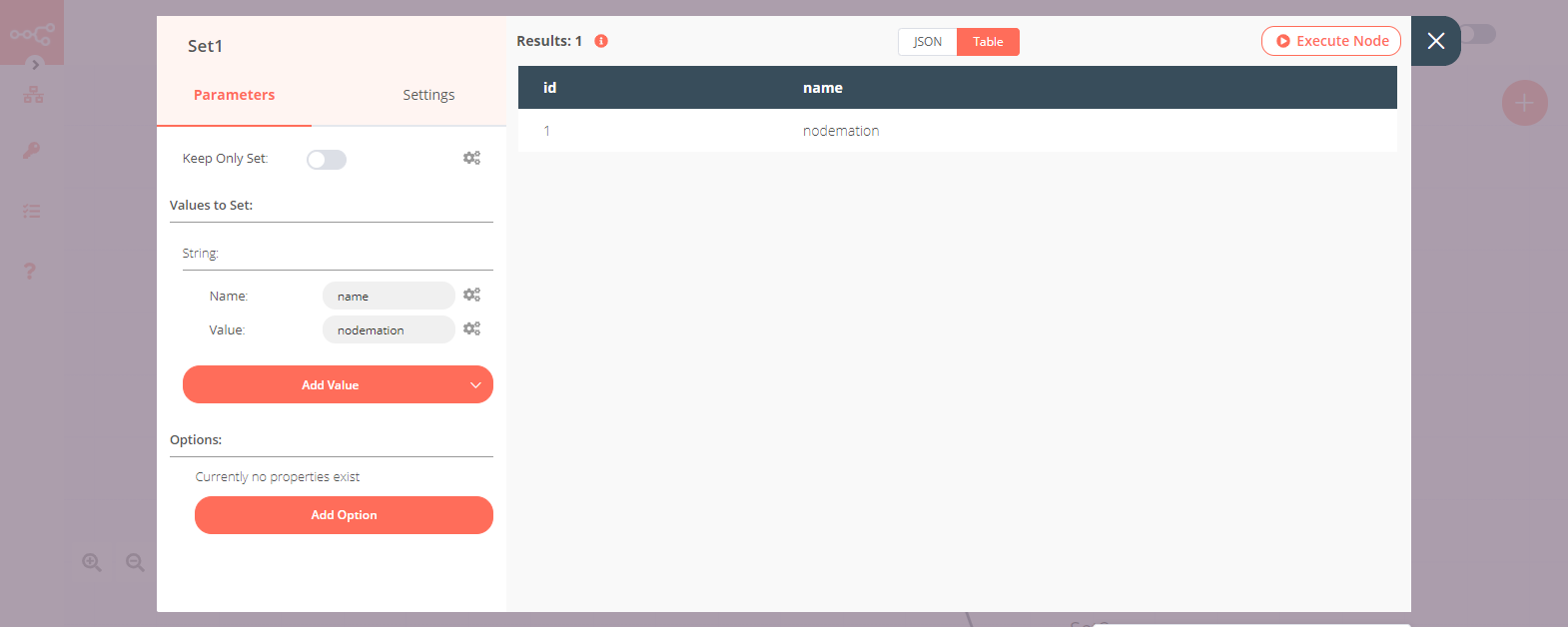
5. Set1 node (for '1' route)#
- Create a Set node connected to the '1' output of the Switch node.
- Click on the Add Value button and select 'String' from the dropdown list.
- Enter
namein the Name field. - Enter
nodemationin the Value field. - Click on Execute Node to run the node.
Note: Notice that only the id with the value 1 made its way to this Set node.
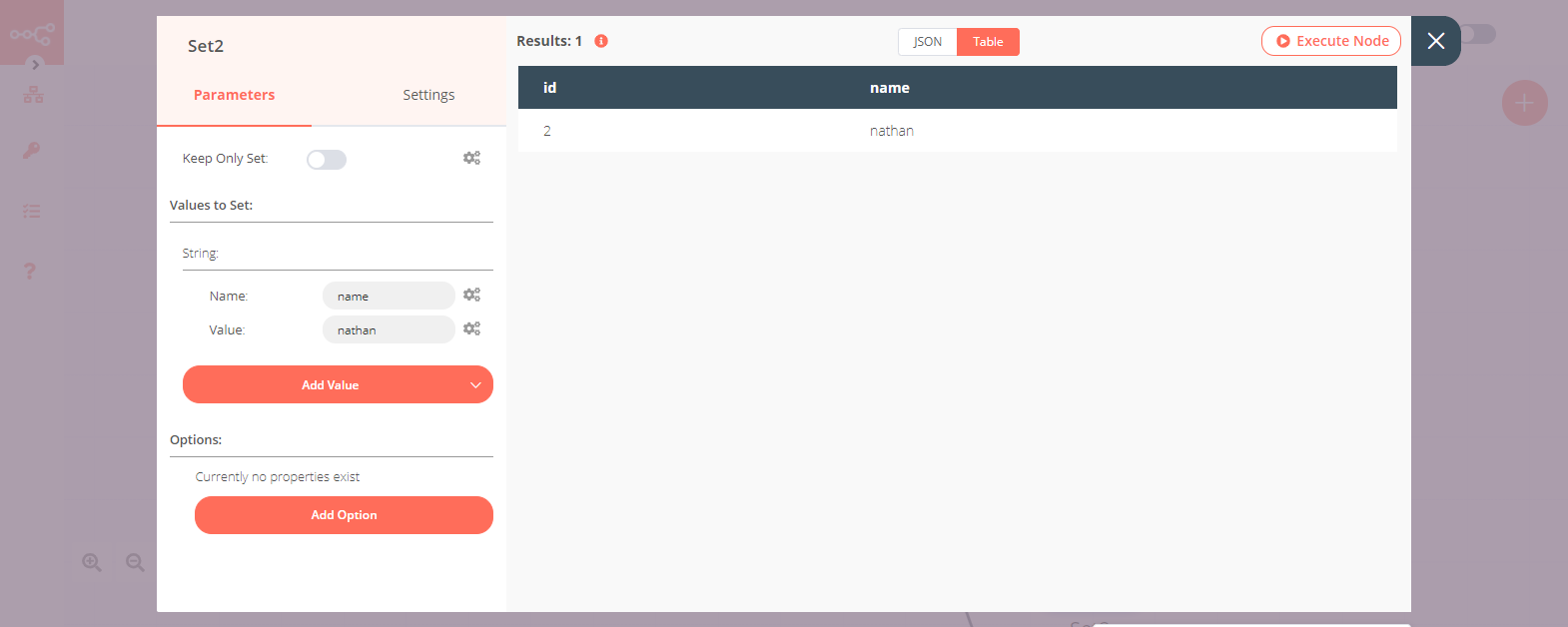
6. Set2 node (for '2' route)#
- Create a Set node connected to the '2' output of the Switch node.
- Click on the Add Value button and select 'String' from the dropdown list.
- Enter
namein the Name field. - Enter
nathanin the Value field. - Click on Execute Node to run the node.
Note: Notice that only the id with the value 2 made its way to this Set node.
7. NoOp node (for '3' route)#
- Create a NoOp node connected to the '3' output of the Switch node.
- Click on Execute Node to run the node.
Note: Notice that none of the ids made their way to this node since the values of the all the ids were either 0, 1, or 2.